
 |
Exam-Style Questions.Problems adapted from questions set for previous Mathematics exams. |
1. | GCSE Higher |
\(ABC\) is a right-angled triangle.
John has a method for finding the length of \(AC\)
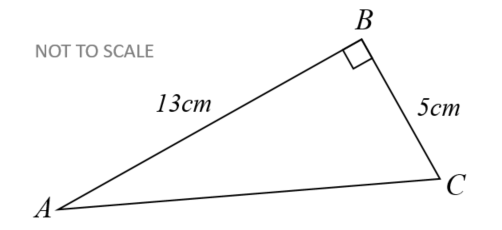 $$AC^2 = AB^2 - BC^2$$
$$AC^2 = 13^2 - 5^2$$
$$AC^2 = 169 - 25$$
$$AC^2 = 144$$
$$AC = \sqrt{144}$$
$$AC = 12$$
$$AC^2 = AB^2 - BC^2$$
$$AC^2 = 13^2 - 5^2$$
$$AC^2 = 169 - 25$$
$$AC^2 = 144$$
$$AC = \sqrt{144}$$
$$AC = 12$$
John's answer of \(12cm\) is not correct.
(a) What mistake has he made with his method?
(b) Show the correct method and the correct answer to 3 significant figures.
2. | GCSE Higher |
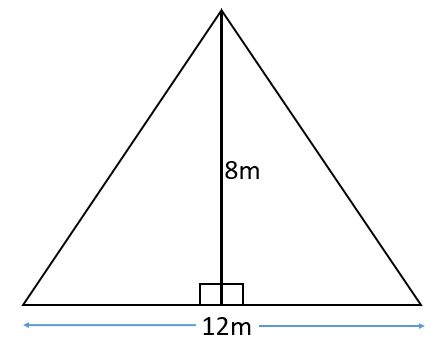
An isosceles triangle shaped frame is made from four pieces of metal. The frame has a height of 8 metres and a base of length 12 metres.
The weight of the metal is 2.5kg per metre. Calculate the total weight of the metal in the frame.
3. | GCSE Higher |
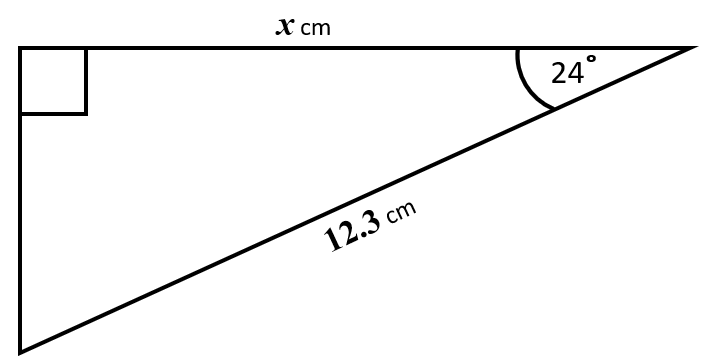
Work out the value of \(x\), the length in centimetres of one of the sides of this right-angled triangle.
Give your answer correct to 1 decimal place.
4. | GCSE Higher |
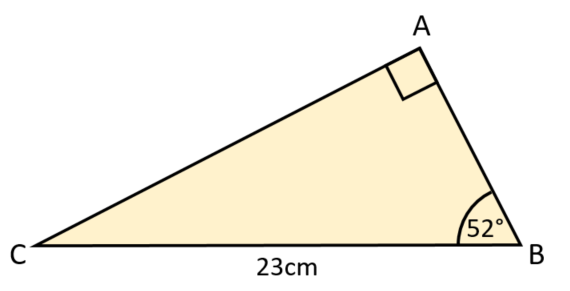
ABC is a right-angled triangle as shown in the diagram below. Calculate the length of AB giving your answer correct to three significant figures.
5. | GCSE Higher |
An arborist sights the top of a tree using a clinometer and reads the angle of elevation to be 29o. Her clinometer is 28 metres from the base of the tree and is on a tripod making it 1.5 metres above ground level.
This diagram is not drawn to scale.
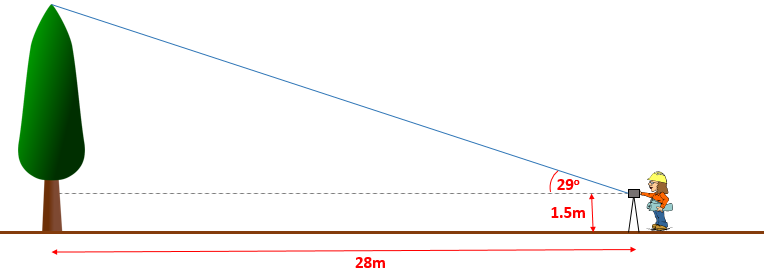
Calculate the full height of the tree.
6. | GCSE Higher |
The diagram shows a right-angled triangle and a semicircle. The straight side of the semicircle is the same length as the longest side of the triangle.
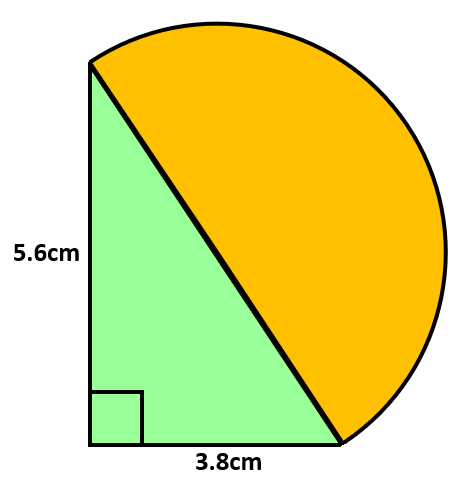
Work out the area of the semicircle.
Give your answer correct to 3 significant figures.
You must show all your working.
7. | GCSE Higher |
The diagram shows a trapezium where the sides AC and BD are parallel.
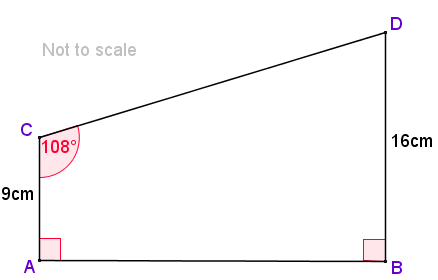
Calculate the length of side CD
8. | GCSE Higher |
Four copies of a green right-angled triangle are used to enclose a yellow square.
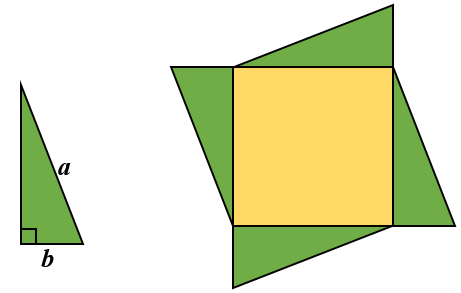
Find the area of the yellow square if the longest side of the green triangle is of length \(a\) cm and the shortest side is \(b\) cm.
9. | GCSE Higher |
The diagram shows a quadrilateral, ABCD, formed from two triangles, ABC and ACD.
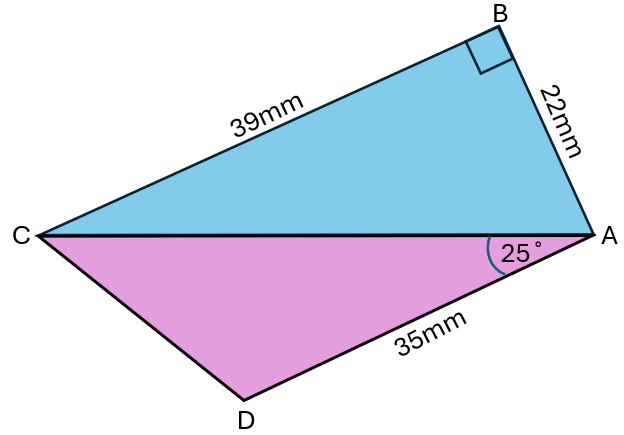
ABC is a right-angled triangle.
(a) Calculate angle BAC.
(b) Calculate BD.
(c) Calculate the shortest distance from D to AC.
10. | GCSE Higher |
A triangular prism is made using two right-angled triangles and three rectangular pieces of cardboard. Five of the vertices have been labeled \(A, B, C, D \text{ and } E\) as shown in the photograph below.
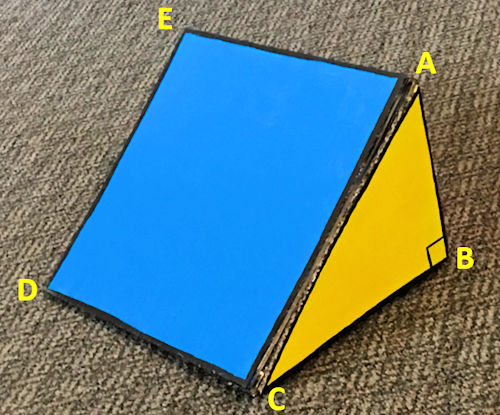
$$ AB = 17cm, \quad BC = 24cm, \quad DC = 28cm $$
Imagine a point \(F\) on the line \(DC\) such that:
$$ DF : FC = 3 : 4 $$Calculate the size of the angle between \(AF\) and the base of the prism.
11. | GCSE Higher |
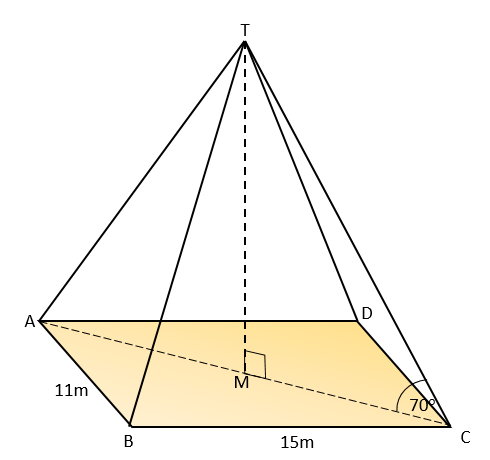
The diagram shows a rectangular-based pyramid, TABCD (not drawn to scale).
The horizontal base ABCD has sides of lengths 11m and 15m. The centre of the base of the pyramid is M.
Angle TMC is 90° and angle TCM is 70°
The volume of a pyramid is \( \frac13 \) × area of base × perpendicular height. Calculate the volume of this pyramid.
If you would like space on the right of the question to write out the solution try this Thinning Feature. It will collapse the text into the left half of your screen but large diagrams will remain unchanged.
The exam-style questions appearing on this site are based on those set in previous examinations (or sample assessment papers for future examinations) by the major examination boards. The wording, diagrams and figures used in these questions have been changed from the originals so that students can have fresh, relevant problem solving practice even if they have previously worked through the related exam paper.
The solutions to the questions on this website are only available to those who have a Transum Subscription.
Exam-Style Questions Main Page
To search the entire Transum website use the search box in the grey area below.
Do you have any comments about these exam-style questions? It is always useful to receive feedback and helps make this free resource even more useful for those learning Mathematics anywhere in the world. Click here to enter your comments.