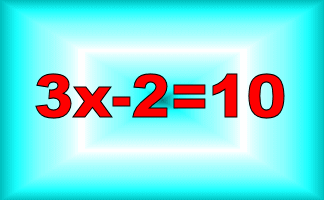Robert Recorde was a Welsh mathematician born around 1512 in Tenby, Wales. He studied at both Oxford and Cambridge universities, which was quite an achievement in his time. As well as being a mathematician, he worked as a doctor and royal physician. Living in the 16th century meant he saw a world of significant changes, with new discoveries in science, exploration, and religion happening all around him.
Robert Recorde is most famous for introducing the equals sign (=) that we use in mathematics today. Before he suggested it, people used longer words or symbols to show that two things were equal. His simple idea, two parallel lines, was meant to represent two things that are the same in length and value. He also wrote books explaining mathematical ideas that are still studied in schools, such as arithmetic and geometry. These works helped standardise how people learned and understood maths for many generations.
Beyond his mathematical achievements, Robert Recorde also contributed to other areas of knowledge. As a physician, he wrote medical texts that explained different health issues and ways to treat them. He was interested in astronomy as well, studying the stars and planets at a time when people were only beginning to understand how our solar system worked. His wide-ranging curiosity showed that he was a true Renaissance man, exploring many different fields during his lifetime.
In summary, Robert Recorde's life and work changed how we do and learn maths, most notably by giving us the equals sign. He also showed that being curious about different subjects—like medicine, astronomy, and other sciences—can lead to exciting discoveries. Recognising his contributions is important because it reminds us that even small inventions, like the equals sign, can have a huge impact on how humanity communicates and learns.
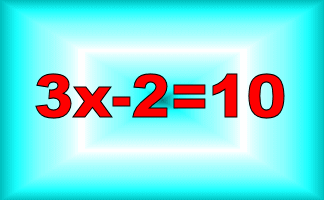
Appreciate the work of Robert Recorde by trying some of the maths that this mathematician is known for.
There is an activity called Equations that you could try right now. A series of exercises, in increasing order of difficulty, requiring you to solve linear equations. The exercises are self marking.
So there's no better time than the present to learn some mathematics from the past: let's Go!