Here are some specific activities, investigations or visual aids we have picked out. Click anywhere in the grey area to access the resource.
 Vector Maze Use vectors to navigate through a maze by the shortest distance.
Vector Maze Use vectors to navigate through a maze by the shortest distance. Vector Cops Help the cops catch the robbers by finding the vectors that will end the chase.
Vector Cops Help the cops catch the robbers by finding the vectors that will end the chase. Vectors An online exercise on addition and subtraction of vectors, multiplication of vectors by a scalar, and diagrammatic representations of vectors.
Vectors An online exercise on addition and subtraction of vectors, multiplication of vectors by a scalar, and diagrammatic representations of vectors.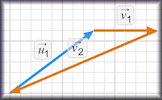 Vector Addition A visual aid showing how vectors can be added and subtracted etc.
Vector Addition A visual aid showing how vectors can be added and subtracted etc.
Here are some exam-style questions on this statement:
- "Find \(4a - b\) as a column vector." ... more
- "Calculate the vector \(3a - 2b\) if the vectors \(a\) and \(b\) are:" ... more
- "(a) Shape \(A\) is translated to shape \(B\) using the vector \( \begin{pmatrix}m\\n\\ \end{pmatrix}\). What are the values of \(m\) and \(n\)?" ... more
- "In the parallelogram OABC two of the sides can be represented by vectors \(a\) and \(c\)." ... more
- "(a) If A is the point (3,5) write down the position vector of A." ... more
- "In the diagram above (not drawn to scale) \(X\) is the point on \(AB\) such that \(AX:XB = 9:4\)." ... more
- "Consider two perpendicular vectors \(p\) and \(q\)." ... more
- "George and Hugo like to fly model airplanes. On one day George's plane takes off from level ground and shortly after that Hugo's plane takes off." ... more
- "The points A and B have coordinates \((3,-2,1)\) and \((4, 0, -1)\) respectively." ... more
- "Consider the vectors \(\mathbf{a}\) and \(\mathbf{b}\) such that \(\mathbf{a} = \begin{pmatrix} 16 \\ -12 \end{pmatrix} \) and \( |\mathbf{b}| = 11\)." ... more
Here is an Advanced Starter on this statement:
Click on a topic below for suggested lesson Starters, resources and activities from Transum.
Furthermore
In the field of mathematics, particularly in vector algebra, a vector is a fundamental concept that represents both magnitude and direction. Vectors can be added or subtracted to form new vectors, and they can also be scaled (multiplied) by a scalar, which changes their magnitude without altering their direction. The magnitude of a vector is a measure of its length.
The key formulae for vectors are:
Vector Addition: \(\mathbf{a} + \mathbf{b} = \begin{pmatrix} a_1 \\ a_2 \end{pmatrix} + \begin{pmatrix} b_1 \\ b_2 \end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix} a_1 + b_1 \\ a_2 + b_2 \end{pmatrix}\)
Vector Subtraction: \(\mathbf{a} - \mathbf{b} = \begin{pmatrix} a_1 \\ a_2 \end{pmatrix} - \begin{pmatrix} b_1 \\ b_2 \end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix} a_1 - b_1 \\ a_2 - b_2 \end{pmatrix}\)
Scalar Multiplication: \(k\mathbf{a} = k \begin{pmatrix} a_1 \\ a_2 \end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix} ka_1 \\ ka_2 \end{pmatrix}\)
Magnitude of a Vector: \(\|\mathbf{a}\| = \sqrt{a_1^2 + a_2^2}\)
Example:
Consider two vectors \(\mathbf{a} = \begin{pmatrix} 2 \\ 3 \end{pmatrix}\) and \(\mathbf{b} = \begin{pmatrix} -1 \\ 4 \end{pmatrix}\).
The sum of \(\mathbf{a}\) and \(\mathbf{b}\) is: $$\mathbf{a} + \mathbf{b} = \begin{pmatrix} 2 \\ 3 \end{pmatrix} + \begin{pmatrix} -1 \\ 4 \end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix} 2 + (-1) \\ 3 + 4 \end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix} 1 \\ 7 \end{pmatrix}$$
If we multiply vector \(\mathbf{a}\) by a scalar, say 3, we get: $$3\mathbf{a} = 3 \begin{pmatrix} 2 \\ 3 \end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix} 3 \times 2 \\ 3 \times 3 \end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix} 6 \\ 9 \end{pmatrix}$$
The magnitude of vector \(\mathbf{a}\) is: $$\|\mathbf{a}\| = \sqrt{2^2 + 3^2} = \sqrt{4 + 9} = \sqrt{13}$$
How do you teach this topic? Do you have any tips or suggestions for other teachers? It is always useful to receive feedback and helps make these free resources even more useful for Maths teachers anywhere in the world. Click here to enter your comments.

