
 |
Pythagoras CoordinatesA self marking exercise on the application of Pythagoras' Theorem. |
Each square on the grid represents one unit. Type your answers to three significant figures if it is not a whole number.
|
What is the length of the line joining the two red points? |
|
|
What is the length of the line joining the two lime points? |
|
|
What is the length of the line joining the two pink points? |
|
|
What is the length of the line joining the two yellow points? |
|
|
What is the length of the line joining the two green points? |
|
|
What is the length of the line segment joining (6, 2) and (1, 3)? |
|
|
What is the length of the line segment joining (8, 4) and (-6, -5)? |
|
|
What is the length of the line segment joining (-3, 0) and (2, -4)? |
|
|
What is the length of the line segment joining (-3, 3) and (-3, -5)? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Finally here's a challenging question to make you really think hard! |
|
InstructionsTry your best to answer the questions above. Type your answers into the boxes provided leaving no spaces. As you work through the exercise regularly click the "check" button. If you have any wrong answers, do your best to do corrections but if there is anything you don't understand, please ask your teacher for help. When you have got all of the questions correct you may want to print out this page and paste it into your exercise book. If you keep your work in an ePortfolio you could take a screen shot of your answers and paste that into your Maths file. |
||
|
|
||
|
|

|
More Activities: |
|
Mathematicians are not the people who find Maths easy; they are the people who enjoy how mystifying, puzzling and hard it is. Are you a mathematician? Comment recorded on the 16 March 'Starter of the Day' page by Mrs A Milton, Ysgol Ardudwy: "I have used your starters for 3 years now and would not have a lesson without one! Fantastic way to engage the pupils at the start of a lesson." Comment recorded on the 9 May 'Starter of the Day' page by Liz, Kuwait: "I would like to thank you for the excellent resources which I used every day. My students would often turn up early to tackle the starter of the day as there were stamps for the first 5 finishers. We also had a lot of fun with the fun maths. All in all your resources provoked discussion and the students had a lot of fun." |
Each month a newsletter is published containing details of the new additions to the Transum website and a new puzzle of the month. The newsletter is then duplicated as a podcast which is available on the major delivery networks. You can listen to the podcast while you are commuting, exercising or relaxing. Transum breaking news is available on Twitter @Transum and if that's not enough there is also a Transum Facebook page. |
|
AnswersThere are answers to this exercise but they are available in this space to teachers, tutors and parents who have logged in to their Transum subscription on this computer. A Transum subscription unlocks the answers to the online exercises, quizzes and puzzles. It also provides the teacher with access to quality external links on each of the Transum Topic pages and the facility to add to the collection themselves. Subscribers can manage class lists, lesson plans and assessment data in the Class Admin application and have access to reports of the Transum Trophies earned by class members. If you would like to enjoy ad-free access to the thousands of Transum resources, receive our monthly newsletter, unlock the printable worksheets and see our Maths Lesson Finishers then sign up for a subscription now: Subscribe |
||
Go MathsLearning and understanding Mathematics, at every level, requires learner engagement. Mathematics is not a spectator sport. Sometimes traditional teaching fails to actively involve students. One way to address the problem is through the use of interactive activities and this web site provides many of those. The Go Maths page is an alphabetical list of free activities designed for students in Secondary/High school. Maths MapAre you looking for something specific? An exercise to supplement the topic you are studying at school at the moment perhaps. Navigate using our Maths Map to find exercises, puzzles and Maths lesson starters grouped by topic. | ||
Teachers | ||
|
If you found this activity useful don't forget to record it in your scheme of work or learning management system. The short URL, ready to be copied and pasted, is as follows: |
Alternatively, if you use Google Classroom, all you have to do is click on the green icon below in order to add this activity to one of your classes. |
It may be worth remembering that if Transum.org should go offline for whatever reason, there is a mirror site at Transum.info that contains most of the resources that are available here on Transum.org. When planning to use technology in your lesson always have a plan B! |
|
Do you have any comments? It is always useful to receive feedback and helps make this free resource even more useful for those learning Mathematics anywhere in the world. Click here to enter your comments. |
||
Close

Level 0 - A 'whole number only' introductory set of questions
Level 1 - Finding the hypotenuse
Level 2 - Finding a shorter side
Level 3 - Mixed questions
Level 4 - Pythagoras coordinates
Level 5 - Mixed exercise
Level 6 - More than one triangle
Level 7 - Harder exercise
Exam Style questions requiring an application of Pythagoras' Theorem and trigonometric ratios to find angles and lengths in right-angled triangles.
Three Dimensions - Three dimensional Pythagoras and trigonometry questions
More on this topic including lesson Starters, visual aids, investigations and self-marking exercises.
Answers to this exercise are available lower down this page when you are logged in to your Transum account. If you don’t yet have a Transum subscription one can be very quickly set up if you are a teacher, tutor or parent.
See the National Curriculum page for links to related online activities and resources.
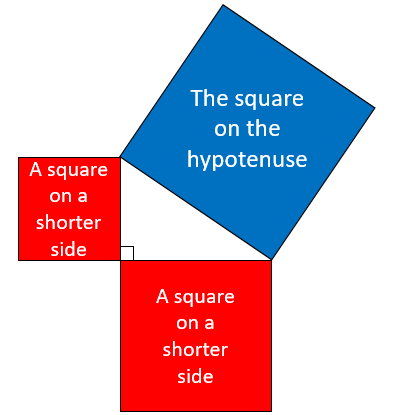
The area of the square on the hypotenuse of a right angled triangle is equal to the sum of the areas of the squares on the two shorter sides.
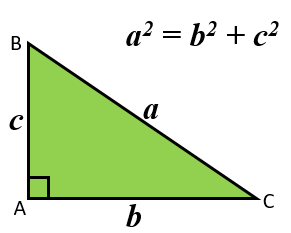
You may have learned the theorem using letters to stand for the lengths of the sides. The corners (vertices) of the right-angled triangle is labelled with capital (upper case) letters. The lengths of the sides opposite them are labelled with the corresponding small (lower case) letters.
Alternatively the sides of the right-angled triangle may me named using the capital letters of the two points they span.
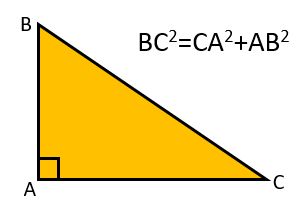
As triangle can be labelled in many different ways it is probably best to remember the theorem by momorising the first diagram above.
To find the longest side (hypotenuse) of a right-angled triangle you square the two shorter sides, add together the results and then find the square root of this total.
To find a shorter side of a right-angled triangle you subtract the square of the other shorter side from the square of the hypotenuse and then find the square root of the answer.
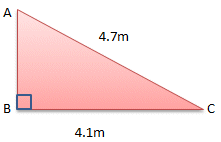
AB2 = AC2 - BC2
AB2 = 4.72 - 4.12
AB2 = 22.09 - 16.81
AB2 = 5.28
AB = √5.28
AB = 2.3m (to one decimal place)
The diagrams aren't always the same way round. They could be rotated by any angle.
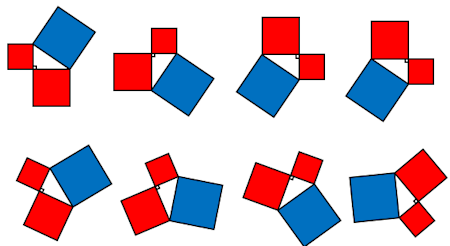
The right-angled triangles could be long and thin or short and not so thin.
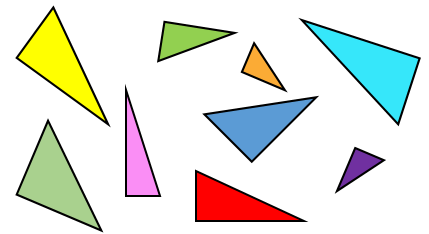
Close
