Here are some specific activities, investigations or visual aids we have picked out. Click anywhere in the grey area to access the resource.
 Standard Form Test your understanding of standard form (scientific notation) with this self-marking quiz.
Standard Form Test your understanding of standard form (scientific notation) with this self-marking quiz. Standard Form Video Learn how to write and calculate with numbers in standard form - sometimes called scientific notation.
Standard Form Video Learn how to write and calculate with numbers in standard form - sometimes called scientific notation.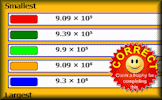 Standard Order Arrange the numbers given in standard form with the smallest at the top and the largest at the bottom.
Standard Order Arrange the numbers given in standard form with the smallest at the top and the largest at the bottom.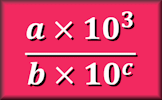 Standard Form Algebra Deeply test your understanding of standard form (scientific notation) by involving a little algebra.
Standard Form Algebra Deeply test your understanding of standard form (scientific notation) by involving a little algebra.
Here are some exam-style questions on this statement:
- "(a) Write 0.0000657 in standard form." ... more
- "The number 1.25 × 10n is a cube number." ... more
- "Work out, giving your answer in standard form," ... more
- "The following table shows the distance from the sun and mass of the eight planets." ... more
- "At a particular time the distance between Earth and Mercury was \(7.7 \times 10^7\) km." ... more
- "A hippopotamus' heart beats approximately \(5.04 \times 10^4\) times in a day when resting. " ... more
- "The volume of the Moon is \(2.2 \times 10^{10}\) km3" ... more
- "The surface gravity, \(g\), of a planet is the gravitational acceleration experienced at its surface. The following formula can be used to find how a planet's gravity compares to Earth's." ... more
- "NASA’s Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) has discovered a planet between the sizes of Mars and Earth orbiting a bright, cool, nearby star. The planet, called L 98-59b, marks the smallest found by TESS yet. The radius of L 98-59b is \(5.42\times 10^6\) m." ... more
Click on a topic below for suggested lesson Starters, resources and activities from Transum.
Furthermore
Numbers in standard form, also known as scientific notation, are expressed as \( a \times 10^n \), where \( 1 \leq |a| < 10 \) and \( n \) is an integer. This notation is particularly useful when dealing with very large or very small numbers, as it allows for a concise representation.
When performing operations with numbers in standard form, it is crucial to follow the rules of arithmetic carefully. Here are some examples to illustrate the operations:
Addition:
When adding numbers in standard form, it is essential to have the same exponent. If the exponents are different, adjust them appropriately before performing the addition.
$$ (3 \times 10^4) + (5 \times 10^3) = (3 \times 10^4) + (0.5 \times 10^4) \\ = 3.5 \times 10^4 $$
Subtraction:
Similar to addition, when subtracting numbers in standard form, ensure that the exponents are the same before performing the subtraction.
$$ (7 \times 10^6) - (2 \times 10^5) = (7 \times 10^6) - (0.02 \times 10^6) \\ = 6.98 \times 10^6 $$
Multiplication:
When multiplying numbers in standard form, multiply the coefficients (the numbers in front of the power of 10) and then add the exponents of the powers of 10.
$$ (12 \times 10^3) \times (4 \times 10^5) = 48 \times 10^8 $$Remember to always express your final answer in standard form, ensuring that the coefficient is a number between 1 and 10 (including 1 but excluding 10). Adjust the power of 10 to compensate any changes you have made to the coefficient.
$$= 4.8 \times 10^9 $$Division:
For division, divide the coefficients and then subtract the exponent in the denominator from the exponent in the numerator.
$$\frac{{3 \times 10^9}}{{6 \times 10^2}} = 0.5 \times 10^7$$
Again remember to always express your final answer in standard form, ensuring that the coefficient is a number between 1 and 10 (including 1 but excluding 10). Adjust the power of 10 to compensate any changes you have made to the coefficient.
$$= 5 \times 10^6$$This video on Scientific Notation is from Revision Village and is aimed at students taking the IB Maths Standard level course.
How do you teach this topic? Do you have any tips or suggestions for other teachers? It is always useful to receive feedback and helps make these free resources even more useful for Maths teachers anywhere in the world. Click here to enter your comments.

